The Future of Liquid-Cooled Split-Unit EV Chargers: Trends, Advantages & Why Choose a Professional Manufacturer
Introduction – Why Liquid-Cooled & Split-Unit Chargers Matter
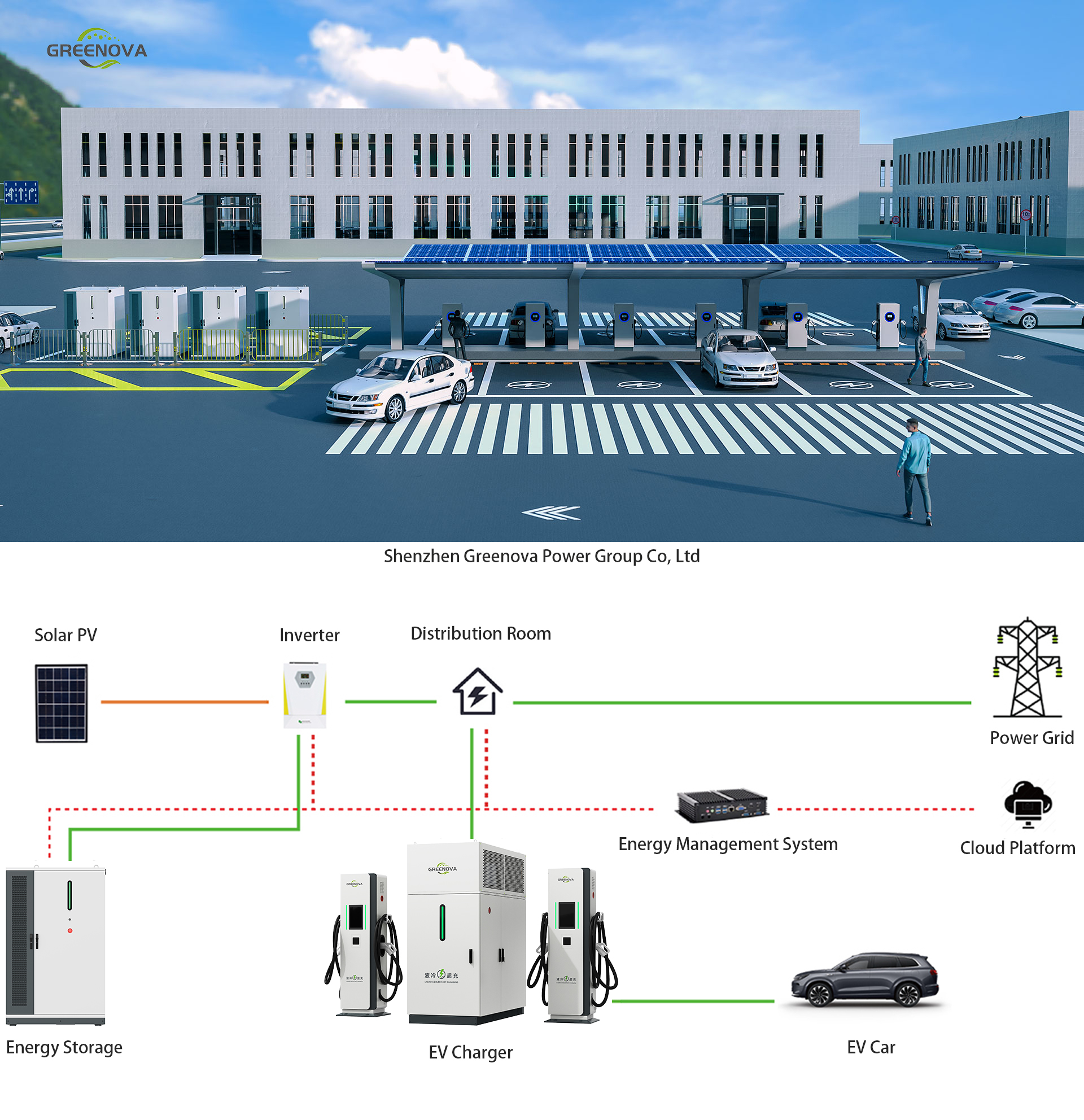
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain rapid adoption worldwide, the demand for faster, safer, and more efficient charging solutions is accelerating. While traditional air-cooled chargers have served early EV infrastructure needs, the rise of high-capacity EV batteries, commercial fleet electrification, and ultra-fast public charging stations requires a new approach. Liquid-cooled split-unit EV chargers are emerging as the next-generation solution — delivering higher thermal efficiency, extended component life, and unparalleled adaptability.
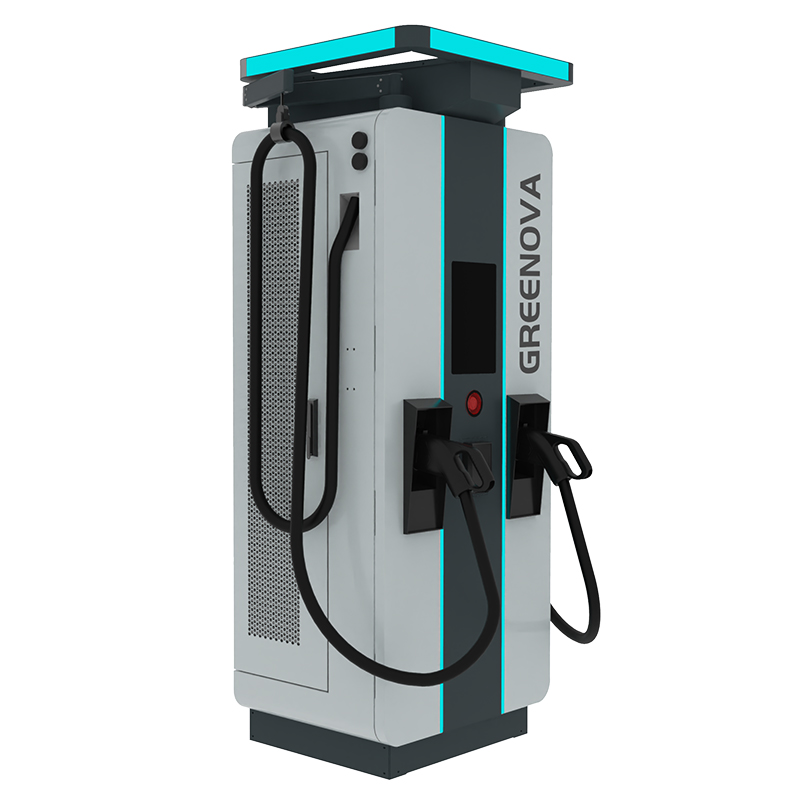
A split-unit charger system typically consists of a centralized power unit (Power Cabinet) and multiple decentralized terminals (Charging Dispensers). When enhanced with liquid cooling, this design offers superior thermal control and operational stability — making it ideal for applications ranging from highway supercharging stations to urban depots and logistics fleets.
In this in-depth article, we explore the global trends driving this technology, the key benefits over traditional systems, and why choosing an experienced manufacturer like Greenova ensures long-term success.
1. Global EV Charging Trends Driving Liquid-Cooled Technology
The global shift toward zero-emission transportation has sparked exponential investment in EV charging infrastructure. Key trends include:
- High-Power DC Charging Demand: EVs with 800V architecture, such as the Porsche Taycan or heavy-duty electric trucks, require 150–350kW (or more) of continuous charging power — something air-cooled systems struggle to deliver efficiently.
- Urban Space Constraints: With limited space for large cooling fans or bulky cables, cities need compact, modular, and scalable solutions.
- 24/7 Fleet Operations: Commercial EV fleets, especially in logistics or public transportation, require chargers that can operate under full load for extended periods with minimal maintenance.
Liquid-cooled split chargers are uniquely positioned to meet these evolving demands by combining scalable architecture with thermal efficiency.
2. Liquid Cooling vs Air Cooling – Key Differences
| Feature | Air Cooling | Liquid Cooling |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Dissipation | Lower, prone to overheating | High, consistent temperature control |
| Noise Level | Noisy due to fans | Quiet operation |
| Charger Lifespan | Shorter due to thermal fatigue | Longer due to stable internal conditions |
| Maintenance Frequency | Higher (dust/fan failures) | Lower (sealed cooling systems) |
| Cost (initial) | Lower upfront | Higher upfront, better ROI long-term |
Liquid cooling enables high-current components to maintain optimal operating temperatures even during peak loads. This translates to consistent output performance, improved safety, and lower total cost of ownership.