As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly mainstream, one question keeps rising in Google’s top auto-related queries: “How do electric car charging stations work?” This article is your in-depth, SEO-optimized guide to EV charging technology—perfect for EV drivers, businesses considering charger installation, or clean energy enthusiasts.
Whether you’re new to the world of electric mobility or evaluating investment opportunities in EV infrastructure, this 8000-character guide will clarify how charging stations work, the types of EV chargers available, and how to capitalize on the fast-growing market.
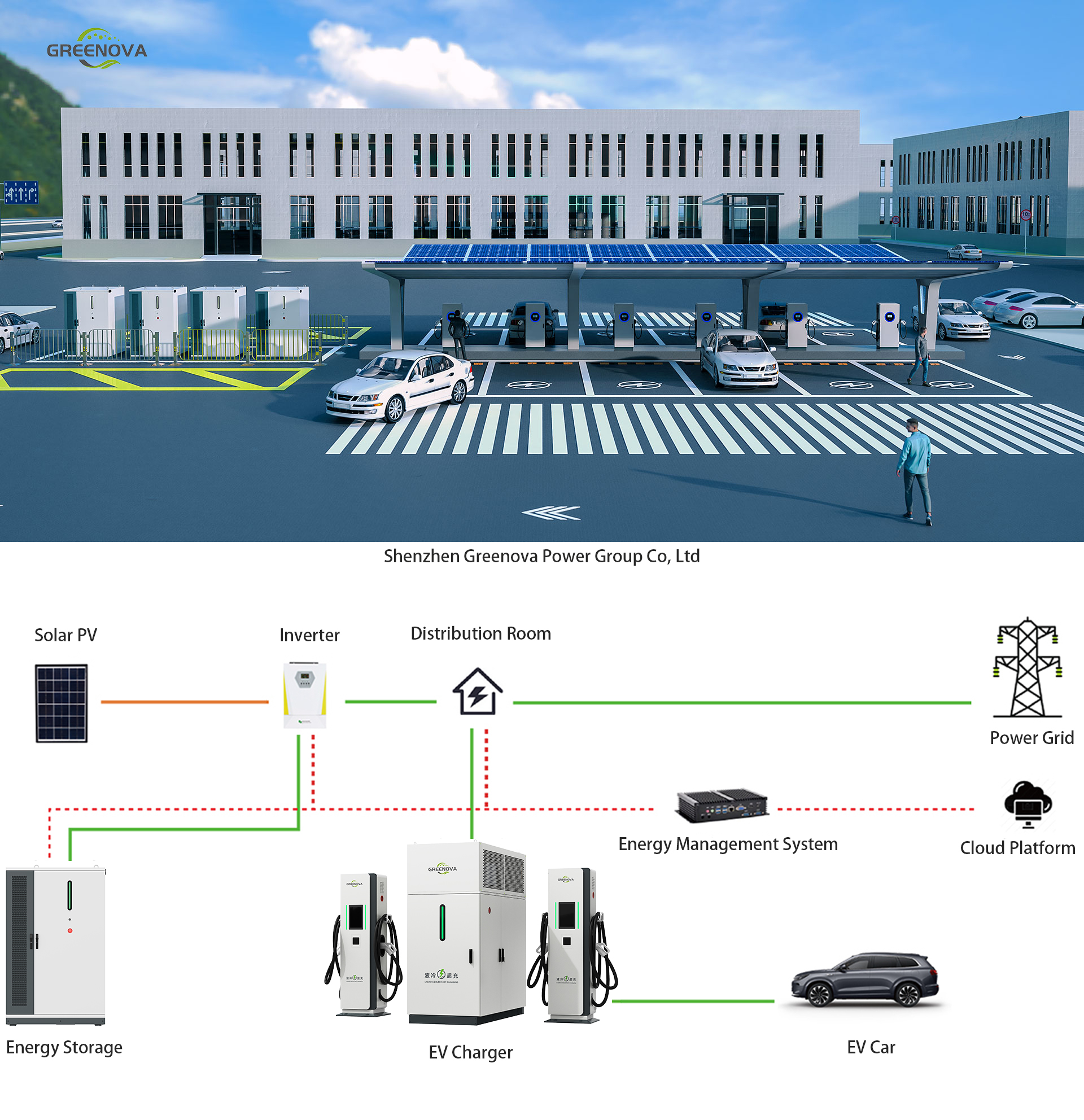
⚙️ What Is an EV Charging Station?
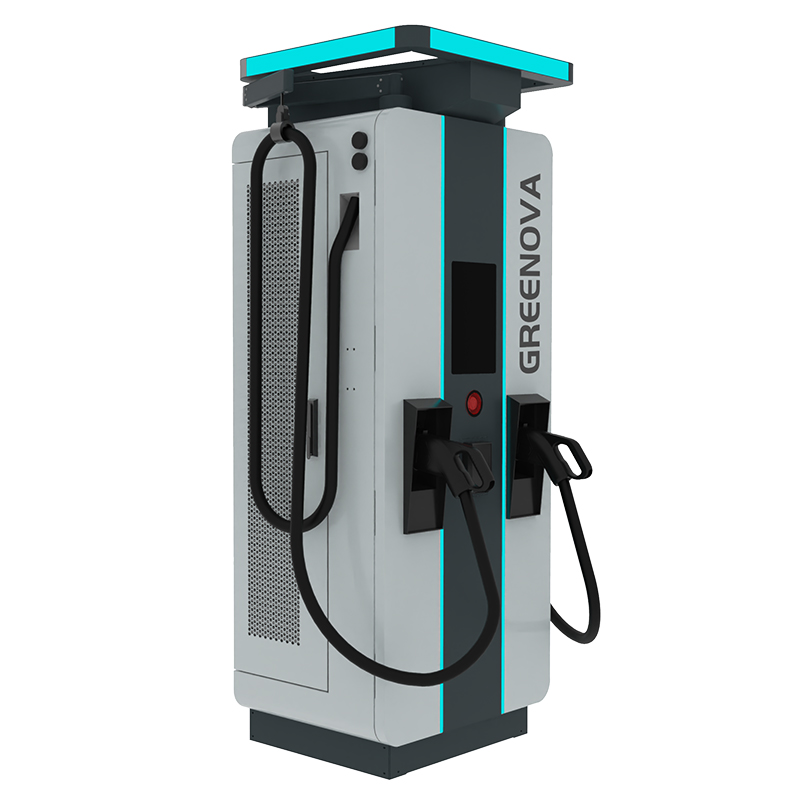
An electric car charging station—also known as Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE)—is a unit that delivers electrical energy to EVs for recharging their batteries. It connects the power source (grid, solar, battery, or hybrid) to the vehicle’s battery pack.
SEO Keywords: electric car charging station, EV charging explained, what is EVSE, EV charger working principle
🔌 How Does an EV Charging Station Work?
- Plug Connection: Users connect their EV to a charger using standardized connectors like CCS (Combined Charging System), CHAdeMO, or Type 2.
- Authentication: Most public EVSE systems require authentication via RFID card, smartphone app, or contactless payment.
- Power Delivery: The station communicates with the vehicle’s Battery Management System (BMS) to determine voltage, current, and safety protocols. Power is then delivered safely.
- Monitoring & Protection: Intelligent chargers monitor charging status, heat, and voltage irregularities to protect both the vehicle and grid.
- Disconnection: Charging ends automatically when the vehicle reaches full charge or the user stops the session manually.
Types of EV Charging Stations
🔹 Level 1: Basic Residential Charging
- Standard 120V AC outlet
- Very slow: Adds about 3–5 miles per hour
- Best for overnight home use
🔹 Level 2: Residential + Commercial Use
- 240V AC
- Medium speed: 10–30 miles per hour
- Suitable for home garages, workplaces, hotels, malls
🔹 Level 3: DC Fast Chargers
- Direct current (DC), high voltage
- Extremely fast: 100–300 km in 20–30 minutes
- Used at highways, commercial hubs, charging stations
SEO Keywords: Level 1 charger, Level 2 EV charger, DC fast charger, EV charging station types
Integration with Renewable Energy
More and more EV chargers are powered by solar and energy storage systems:
- Solar-powered EV chargers reduce reliance on the grid
- Battery energy storage supports night-time and off-peak charging
- Hybrid systems (solar + battery + grid) ensure consistent power and energy cost savings
SEO Keywords: solar EV charger, solar energy for EV, battery storage EV charging
Smart Charging and V2G
Modern charging stations come equipped with smart technology and bidirectional functionality:
Smart Charging Features
- Load balancing
- Scheduled charging during off-peak hours
- App-based control
- Remote diagnostics and updates
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Capability
- EVs feed energy back to the grid during peak times
- Grid stability and revenue for EV owners
- Maximizes return on investment for businesses
SEO Keywords: smart EV charging, V2G technology, bidirectional EV charger, dynamic load management
Who Uses EV Charging Stations?
➤ Homeowners
- Daily charging convenience
- Reduced fuel costs
- Property value increase
➤ Businesses & Retailers
- Attract EV customers
- Meet ESG goals
- Offer paid charging as a service
➤ Fleet Operators & CPOs
- Cut fleet fuel costs
- Monitor and manage usage
- Transition to low-emission operations
SEO Keywords: home EV charger, business EV charging, fleet EV charger, charge point operator
Installation Considerations
When installing an EV charging station, keep in mind:
- Location: Near parking, accessible to all users
- Power Supply: Sufficient amperage and voltage
- Permits and Compliance: Local regulations, safety standards
- Connector Type: Compatible with most EV models
- Scalability: Future-proof infrastructure
SEO Keywords: EV charger installation, EV charger compliance, public charging infrastructure
EV Charging FAQs
Q1: How long does it take to charge an electric car? A: From 30 minutes (DC fast) to 12 hours (Level 1), depending on battery size and charger power.
Q2: Are EV charging stations free? A: Some are free (usually government or retail-sponsored); others charge per kWh or session.
Q3: Can I install a charger at home? A: Yes. Level 2 home chargers are common and supported by many incentive programs.
Q4: What are the costs? A: Costs range from a few hundred dollars (Level 1) to several thousand (Level 3), plus installation.
Q5: Which plug types are supported? A: Most stations support CCS, CHAdeMO, and Type 2; adapters are available for Tesla and other models.
Why Now Is the Time to Invest in EV Charging
With electric car adoption soaring and governments offering financial support, the demand for EV infrastructure is accelerating. By installing or reselling EV charging stations today, you:
- Future-proof your property or business
- Tap into a high-growth clean energy sector
- Support global carbon reduction goals
Whether you’re looking to add a charger at home, become a charge point operator, or start an EV-focused business, the EV charging wave is here—and it’s only gaining momentum.
Call to Action
Ready to explore the best EV charging solutions for your needs?
Contact Greenova today for:
- DC fast chargers (30–240kW)
- V2G-enabled smart chargers
- Solar + Storage + Charging integrated systems
- Global shipping & technical support
how do electric car charging stations work, EV charging station, EV charger installation, smart EV charger, DC fast charger, solar EV charging, V2G charging, bidirectional EV charger, EVSE system, EV charging types, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, home EV charger, commercial EV charger, EV fleet charging, CCS EV charger, CHAdeMO, Type 2 EV plug