1. Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) are no longer niche. Governments, corporations, and consumers are aligning to decarbonize transport, reduce fossil fuel dependence, and comply with net-zero goals. As vehicle electrification accelerates, charging infrastructure becomes the backbone of that transformation. The question is not if, but how fast, how broadly, how reliably and at what cost we can scale up global EV charging infrastructure.
This article analyses where the EV charging market is headed globally: macro trends, forecasts, key challenges, and emerging opportunities. It also spotlights Greenova, a rising manufacturer and solutions provider, to understand how companies like Greenova are positioned to contribute meaningfully, and what strategic moves will matter going forward.
2. Global EV Adoption Trends
-
EV sales continue growing rapidly. Forecasts suggest tens of millions of new EVs sold annually by the mid-2030s. ABI Research
-
In many countries, EVs are becoming a dominant share of new vehicle sales, driven by policy mandates, incentives, tightening emissions standards. Regions like Asia-Pacific are among the fastest growing. ABI Research+1
-
Consumer behaviors are shifting: range anxiety, availability of public fast charging, time-to-charge, total cost of ownership are becoming important decision points. Charging at home remains important, but public and on-the-go charging infrastructure is rising in importance. PwC+1
3. Key Drivers & Challenges in Charging Infrastructure
Drivers
-
Policy & Regulation: Many governments are offering subsidies, mandates for zero emissions, or requiring infrastructure deployment (public, workplace, multi-unit residences).
-
Grid & Energy Transition: Integration with renewables (solar, wind), energy storage, grid management (peak shaving, load balancing) is becoming essential.
-
Fleet Electrification: Commercial fleets, ride-hailing, public transit require fast, reliable, high-capacity charging.
-
Consumer Expectations: Faster charging, universal compatibility, reliability, and lower cost per kWh drive demand.
Challenges
-
Cost & Capital Expenditure: Building fast chargers (especially ultra-fast / DCFC) is expensive: hardware, grid upgrades, installation, permitting.
-
Grid Capacity & Stability: Especially in developing regions, or in rural / remote areas, grid supply may be weak or unreliable.
-
Standards & Interoperability: Different connector standards (CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T, etc.), payment/ID/authentication systems, communication protocols (e.g. OCPP) raise complexity.
-
Operational Complexity & Maintenance: Ensuring uptime, safety, consistency, and managing varying usage patterns requires good design and service.
-
Site & Real Estate Constraints: Finding locations, parking, land-use, permits, utility access, demand estimation etc.
4. Market Size, Forecasts & Emerging Opportunities
-
According to Grand View Research, the global EV charging infrastructure market is expected to reach around USD 125.39 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of ~25.5% from mid-2020s onward. 格兰德视野研究
-
Market research (Ken Research) forecasts the global EV charging station market will reach USD 155 billion by 2029, driven by EV sales growth, stronger policies, and technological advancement. Ken Research
-
In the US, PwC estimates that EV supply equipment (EVSE) must grow nearly ten-fold by 2030 to meet the needs of projected 27 million EVs, from roughly 4 million charging points up to about 35 million. PwC
-
Public charging is forecasted to become a major revenue generator. ABI Research predicts public charging revenue globally may increase from about US$16.4B in 2025 to over US$152B by 2035. ABI Research
Emerging opportunities include:
-
Ultra-fast charging (> 150-350 kW and beyond), reducing charging times to under 20 minutes at public highway stations. Ken Research
-
Integration with renewable energy & storage: solar + battery storage co-located with charging stations to reduce grid strain and operational costs. Ken Research+1
-
Mobile / off-grid charging solutions (portable, trailer-based, emergency charging) that can serve remote, temporary, or underserved locations.
-
EV Charging as a Service (CaaS) models for fleet operators and municipalities, with upfront costs shifted and risk managed by service providers. Mordor Intelligence
5. Technological Innovation & Standards
-
Connector / Protocol Compatibility: Supporting multiple standards (CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T etc.) is increasingly important for global manufacturers.
-
Communication Protocols: Open standards like OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) are crucial for interoperability of chargers and back-end systems.
-
Smart Charging & Grid Integration: Features like dynamic load balancing, demand response, vehicle-to-grid or vehicle-to-home are being researched / piloted.
-
Energy Storage & Renewable Integration: Solar-powered, storage-augmented chargers reduce reliance on grid upgrades and can help manage peak demand.
-
Modular & Scalable Hardware Design: Allows for upgrading power levels, modular maintenance, and cost optimization.
6. Regional Comparisons: Asia-Pacific, Europe, Americas
| Region | Strengths / Tailwinds | Constraints / Gaps | Key Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific (especially China, Southeast Asia) | Massive automotive markets, growing EV adoption, strong government subsidies, existing manufacturing base. | Grid constraints in remote/rural areas, diversity of standards, sometimes weaker regulatory frameworks or inconsistent enforcement. | Rapid deployment of chargers, domestic OEM competition, solar + storage integration, localized innovations. |
| Europe | Strong regulatory push (EU Green Deal, emission targets), high environmental awareness, incentives, high grid reliability. | High cost of labour/installation, land/use / permitting constraints, high electricity cost in some countries. | Ultra-fast corridors (150-350 kW+), interoperability / roaming across countries, emphasis on renewable sources. |
| Americas (USA, Canada, Latin America) | Strong investment programs, high demand for long-distance travel, fleets, commercial / highway charging. | Disparities in infrastructure between urban and rural, regulatory/policy uncertainty, permitting delays. | Federal/institutional funding, expansion of fast-charging networks, integration with utility programs. |
7. Business Models & Policy Landscape
-
Public-private partnerships are common: governments often offer incentives, grants, subsidies or regulatory support.
-
Charging service providers / charge point operators (CPOs) increasingly take on multiple roles: installation, operation, maintenance, customer experience, billing.
-
Utility involvement: utilities often participate in investments, demand-management programs, or operate chargers themselves.
-
EV charging as a service (CaaS): subscribers, fleet operators, municipalities can procure charging capacity without large capex. Mordor Intelligence
-
Regulatory support needed: Incentives for installation; streamlined permitting; standards and codes; rebates; grid incentives.
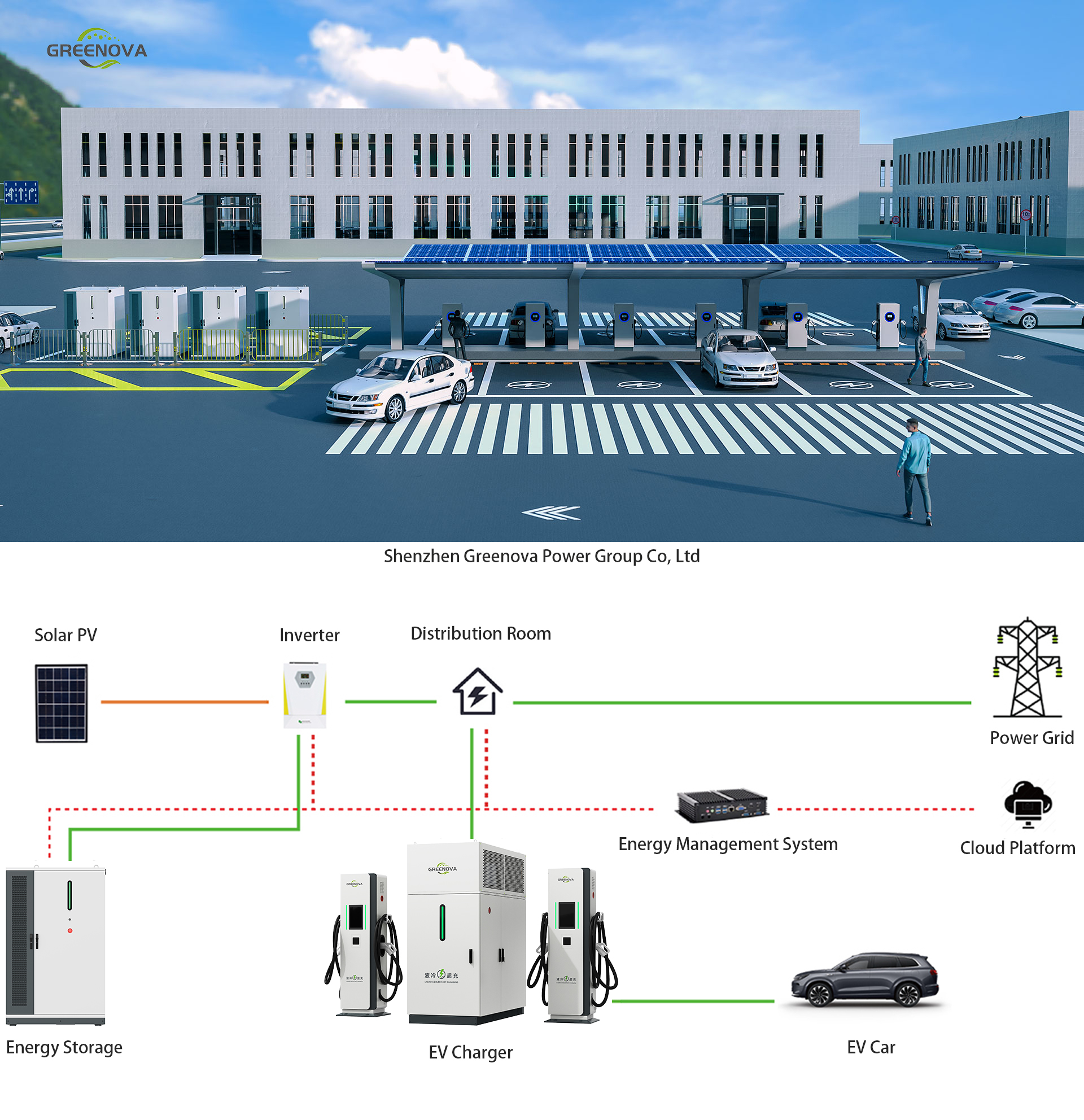
8. Greenova: Overview, Strengths, Product Portfolio
Here is a detailed look at Greenova (Shenzhen Greenova Power Group) — its history, capabilities, what differentiates it, and what products it brings to the table.
Company Overview & Credentials
-
Greenova is a manufacturer of EV chargers and energy solutions, with its operations centered in China. It has R&D, design, production, and sales capabilities. GreenOvaCharger+1
-
It supports OEM & ODM services; has a large R&D technical team (80+ engineers) and an industrial base (~30,000 square meters). Annual production capacity exceeds 200,000 sets. GreenOvaCharger+1
-
Products have passed multiple international certifications (CE, RoHS, CCC, TÜV, etc.) and support international standards and protocols. GreenOvaCharger+1
Product Range & Innovation
Greenova offers a broad spectrum of EV charger products and supporting solutions. Key product categories include:
-
AC & DC chargers, from small wall-mount/portable units (home, small business) to large fast charging stations. Power levels range from ~3.5 kW up to 720 kW for DC fast chargers. greenovapower.com+1
-
Portable / mobile charging units, off-grid solutions (with battery storage), solar-integrated chargers. GreenOvaCharger+2GreenOvaCharger+2
-
Split DC fast chargers, universal compatibility (multiple connector types: CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T) to serve various vehicle models. greenovapower.com+1
-
Integrated energy storage + PV backup chargers: for locations with unreliable grid or high demand peaks. GreenOvaCharger
Strengths & Competitive Advantages
-
One-stop solution: from design, R&D, manufacturing to service. Minimizes dependencies and can accelerate time to market. greenovapower.com
-
Customization: OEM/ODM support and flexibility to tailor hardware & configuration for different regions or use-cases.
-
Quality / Standards: Multiple certifications, testing, reliability focus.
-
Global reach: Greenova has exported products to markets including Europe, Japan, Southeast Asia, South America, etc. GreenOvaCharger+1
9. How Greenova Fits into Future Infrastructure Scenarios
Given the trends and forecasts, here is how Greenova is well placed, and how it might evolve to capture more of the opportunity.
| Scenario | How Greenova Already Supports / Aligns | Opportunities & Gaps to Leverage / Fill |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid roll-out of ultra-fast highway chargers | Greenova has DC fast chargers up to hundreds of kW; supports multiple connector types, certifications, etc. | Push further into ultra-fast (>350-500kW), ensure grid and cooling/thermal systems are robust; develop partnerships with highway service operators. |
| Renewable + storage-integrated charging stations | Greenova offers PV + storage integrated stations; off-grid / mobile storage chargers. | Scaling battery storage capabilities, reducing cost, optimizing control systems, smart energy management, charging during green energy peaks. |
| Fleet electrification (buses, delivery, logistics) | Greenova has high-power DC chargers, modular designs, multiple connector compatibility. | Tailoring solutions for heavy-duty EVs, offering robust maintenance / uptime guarantees, integrating with fleet management software and telemetry. |
| Emerging markets & remote / rural areas | Mobile/off-grid units; modular / scalable hardware; flexible deployment. | Address logistical, climate, supply chain, and training/service challenges in remote zones; ensure support infrastructure and local servicing. |
| Charging as a Service / Subscription & Management Platforms | Many products support OCPP and overseas deployment; quality control is strong. | Expand software/backend services; partner or develop charge point operations platforms; offer financing/lease models; improve payment & user experience. |
10. Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
For Greenova
-
Invest in ultra-fast charging R&D: Higher power DC-FC, better cooling, thermal management, and durability will be essential as demand for quick charging grows.
-
Enhance software and network services: Charging infrastructure isn’t just hardware — reliability, uptime, payment, user interface, monitoring are all critical. Strengthen backend platforms, remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance.
-
Expand partnerships: With utilities, governments, fleets, highway / retail operators to secure prime locations and support for grid upgrades.
-
Localization & service networks: To succeed globally (especially in Europe, Americas, developing nations), local service, spare parts, technical training, and support are vital.
-
Sustainability credentials: Emphasizing green components, renewable energy integration, lifecycle / recycling of hardware, low carbon footprint — this appeals to both regulators and customers.
For Governments / Regulators
-
Streamline permitting and approval processes for charger installation.
-
Provide incentives and subsidies not just for EV purchase but for charger deployment, especially in underserved areas.
-
Standardize connectors / payment / communication protocols to reduce fragmentation and improve user experience.
-
Support grid upgrades where needed; encourage renewable plus storage integration.
-
Encourage public-private models and innovative funding (CaaS, PPPs).
For Investors / Charge Point Operators (CPOs)
-
Focus investment where demand is growing: highways, fleet depots, workplace charging.
-
Consider total cost of ownership, not just upfront cost — uptime, maintenance, energy costs, grid fees matter.
-
Prioritize chargers with universal compatibility and flexibility (e.g. multi-standard connectors).
-
Evaluate energy sources, storage, and demand management to reduce operational costs and grid strain.
11. Conclusion
The transformation to electric mobility is accelerating. The world needs robust, reliable, fast, and widespread charging infrastructure. Several markets will see explosive growth over the coming decade, especially for fast / ultra-fast chargers, fleet charging solutions, renewable energy integration, and service-oriented models.
Greenova is positioned as a strong contender: broad product range (from portable/off-grid to high-power DC fast chargers), solid certifications, OEM/ODM flexibility, and global reach. To maximize its impact and market share, Greenova should continue investing in ultra-fast charging, backend software & service, and establishing a strong global service and partnership network.
For all stakeholders — manufacturers, operators, governments, and investors — the opportunity is huge. The decarbonization goals demand rapid infrastructure build-out. Companies that combine hardware excellence, reliability, scalability, and sustainable deployment will lead the charge.